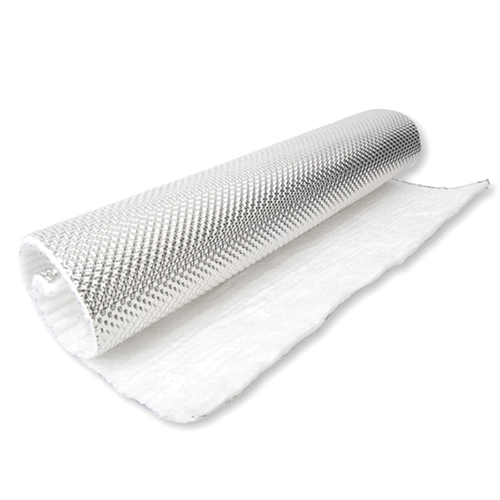
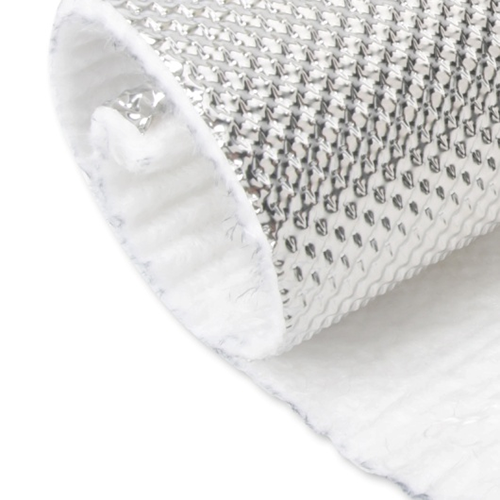
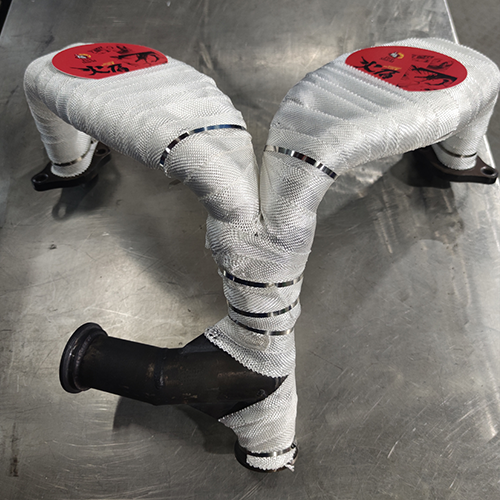
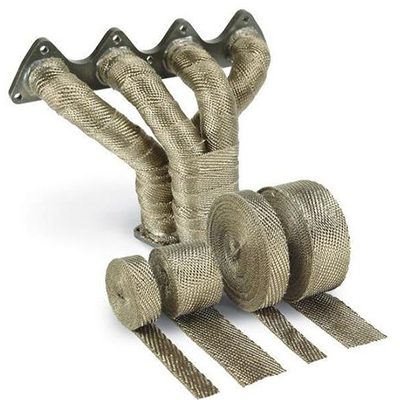
Hiwowsport Wastegate Blankets are designed to help minimize the heat soak transfer between the main body and actuator body of the wastegate. In doing so, we can help alleviate actuator diaphragm stress while in use, especially under extreme loads, due to extreme heat and dramatic temperature fluctuations. Results will be a more stable operation of the wastegate valve allowing consistent performance of the turbocharger. Another key benefit of the PTP Wastegate Blanket is to protect any nearby lines or components from the heat on the main body of the wastegate.

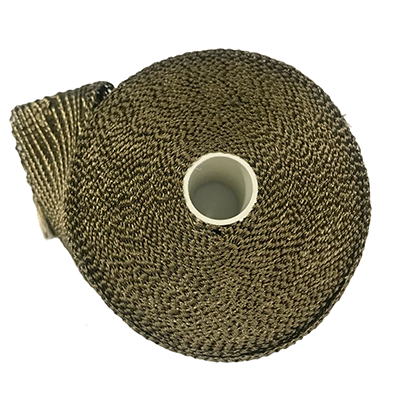
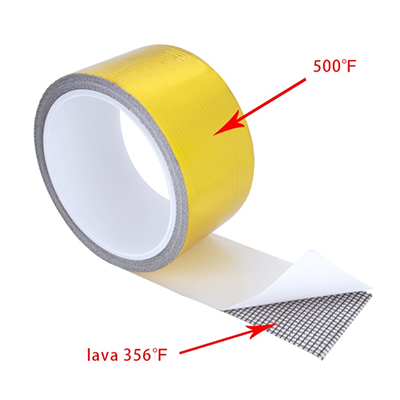
The Wastegate Blankets are constructed with an outer layer made from pulverized volcanic lava rock (Rated 1800°F Direct Heat / 2500°F Radiant Heat) formed into fabric and woven into a tight mesh weave. These wastegate blankets are internally insulated with high temperature calcium magnesium silicate wool (Rated 1832°F Continuous / 2300°F Peak) overlaid with a high temperature stainless steel mesh for increased durability and improved thermal resistance. The Lava Wastegate Blankets are designed to withstand the harshest of conditions.