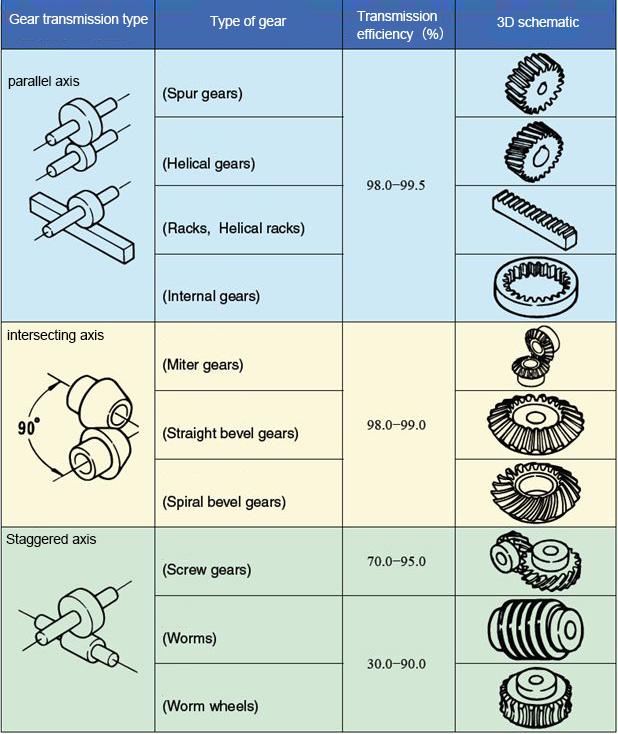
The rise and fall of the price of silicone rubber is mainly related to methyl vinyl silicone rubber (raw rubber raw material), because raw rubber is the main raw material for the production of silicone rubber.
Secondly, it is also related to factors such as tensile strength of silicone raw materials, hardness of silicone raw materials, different types and varieties of silicone raw materials, logistics and transportation costs, and market supply and demand.
1. The raw rubber is mainly produced from raw rubber, so the price change of raw rubber is the main factor affecting the price of raw rubber. And the price of raw rubber is quoted according to the weekly market changes, and the price of raw rubber varies greatly. Today, the price of silica gel raw materials is still running at a high level.
2. The tensile strength of silicone raw materials, when customers purchase silicone raw materials, the quality is mainly based on the tensile strength. The quality system of silica gel raw materials is mainly divided into three types: powder glue, precipitation glue and gas-phase glue. Powder glue is produced by adding a certain proportion of silica powder. It is produced by fumed silica, the tensile strength is 6Mpa-8Mpa, the quality and price are moderate, and it is the most widely used; fumed silica is produced from fumed silica. The produced fumed adhesive has good tensile strength and transparency. The tensile strength is generally 7Mpa-9Mpa, which is expensive and generally only used for high-standard products.
3. The price of silicone raw materials with different hardness is also different, because the higher the hardness, the lower the glue content, and the lower the hardness, the higher the glue content. Therefore, the higher the hardness in the precipitation glue, the cheaper the price. The higher the hardness in fumed rubber, the more expensive the price is because the price of precipitated silica is lower than that of raw rubber, while the price of fumed silica is higher than that of raw rubber.
4. Silica gel raw materials are divided into different models according to their functional uses, mainly divided into food grade silica gel, high temperature resistant silica gel, insulating silica gel, flame retardant silica gel, sulfur-added color silica gel, etc. The auxiliary materials added are also different, so the price of silicone raw materials of different models is also different.
5. The cost of logistics and transportation also slightly affects the price of silica gel raw materials. It mainly depends on the distance of transportation. The closer the distance is, the more affordable the price is. On the contrary, the price of silica raw materials should be appropriately increased for the farther the distance.
6.The price increase is still related to market supply and demand. If the market is prosperous, it will lead to a surge in silicone rubber compound raw materials.
Nowadays, the sales market of silicone raw materials is very clear, and many manufacturers charge shoddy products in order to increase sales. Customers will be deceived if they pursue affordable prices. As the saying goes, you get what you get for every penny. This sentence is just right for silicone raw materials. Only good quality, affordable price, and high-quality service can meet the basic needs of users.