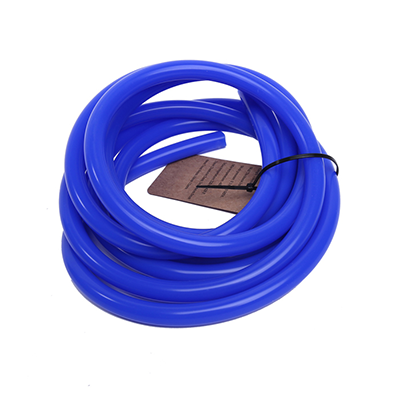
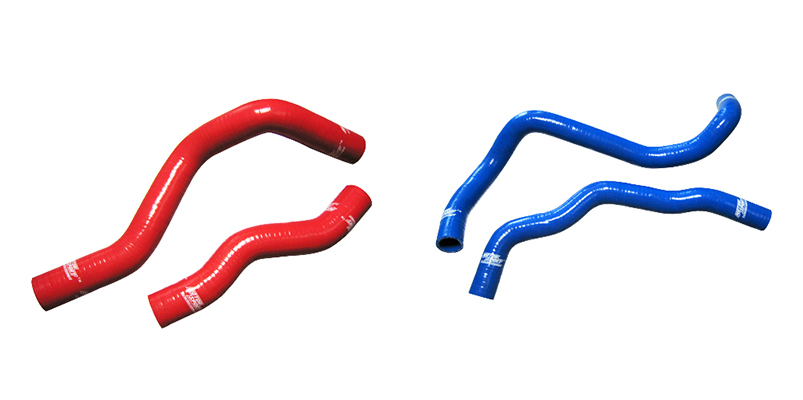
Silicone vacuum tube is designed for vacuum advance, windshield washer fluid, transmission modulator, and emission control. Available in sizes from BoreXWall 1/8”X5/64”, 5/32”X5/64”, 3/16”X3/32”, 1/4”X3/32”, 5/16”X1/8” to 3/8”X1/8”.
Silicone is resistant to hardening, cracking, ozone attack, sunlight, moisture, steam, dust, aging, various pressure ranges, and to many chemicals too. Additional advantages of Silicone are it is easier to install and run than ridged pipe, is not subject to corrosion, stress, or cracking, and it absorbs engine movement and vibration.
Features and Benefits of Silicone Hose:
-Resistant to a wide range of temperatures
-Resistant to hardening, cracking, ozone attack, sunlight
-Resistant to moisture, steam, dust, aging, various pressure ranges
-Resistant to many chemicals
-Retains flexibility in hostile engine environments
-Excellent electrical insulating properties
-Longer life than EPDM (Black Rubber)