There are many kinds of gears, and the most common classification method is according to the gear shaft. Generally divided into three types: parallel axis, intersecting axis and staggered axis.
1) Parallel shaft gears: including spur gears, helical gears, internal gears, racks and helical racks, etc.
2) Intersecting shaft gears: there are straight bevel gears, spiral bevel gears, zero-degree bevel gears, etc.
3) Staggered shaft gears: there are staggered shaft helical gears, worm gears, hypoid gears, etc.
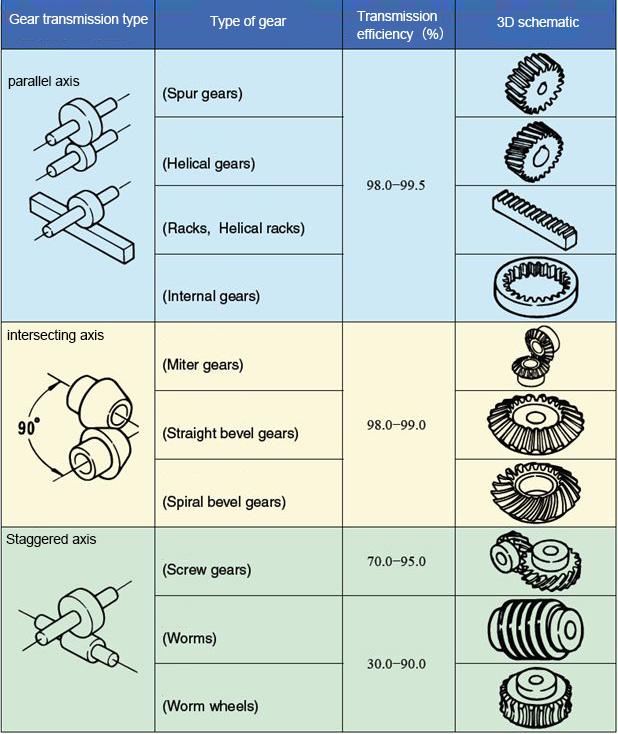
The efficiency listed in the table above is the transmission efficiency, excluding the loss of bearing and stirring lubrication. The meshing of the gear pairs of the parallel shaft and the intersecting shaft is basically rolling, and the relative sliding is very small, so the efficiency is high. Staggered shaft helical gears, worm gears and other staggered shaft gear pairs, because the relative sliding generates rotation to achieve power transmission, so the impact of friction is very large, and the transmission efficiency is reduced compared with other gears. The efficiency of a gear is the transmission efficiency of the gear under normal assembly conditions. If there is an incorrect installation, especially if the bevel gear is not assembled at the correct distance, resulting in an error in the intersection of the same cone, its efficiency will drop significantly.
